

Blepharospasm in Adults
In treatment-naïve patients*
XEOMIN Demonstrated Significant Improvements in the Jankovic
Rating Scale (JRS) Severity Subscore vs Placebo1,2
- XEOMIN 50 U demonstrated significant improvements when compared with placebo at Week 6 (P=0.0004)1,2
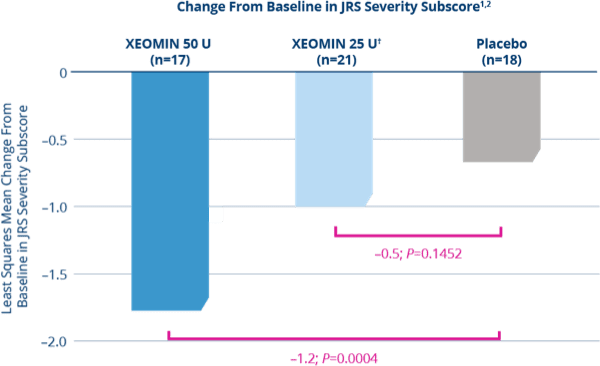

*Patients were defined as treatment-naïve if at least 12 months had passed since their last botulinum toxin treatment for blepharospasm.
†XEOMIN 25 Units was not statistically significant when compared with placebo at Week 6 (P=0.1452)1,2
Pivotal Trial Design in Treatment Naïve Patients
Randomized, Double-blind, placebo-controlled
Trial of XEOMIN in Patients with
Blepharospasm1
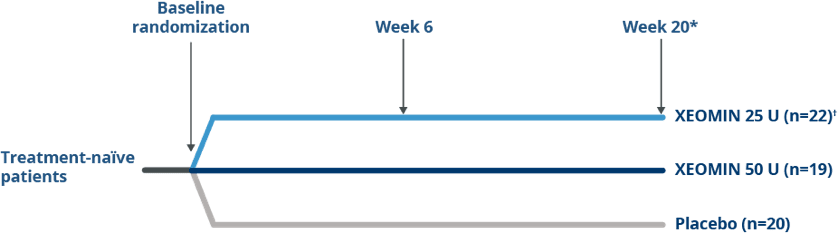

*At the end of the initial 20-week placebo-controlled phase, patients had the option to enroll in an open-label extension if they had a confirmed need for a re-injection.
†XEOMIN 25 U was not statistically significant when compared with placebo at Week 6 (P=0.1452)
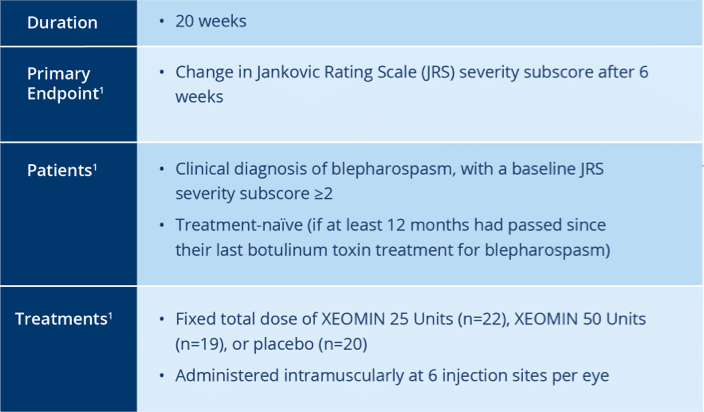

Studied in nearly 400 patients with
blepharospasm in clinical trials worldwide2
References
- Mitsikostas DD, Dekundy A, Sternberg K, Althaus M, Pagan F. IncobotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of blepharospasm in toxin-naïve subjects: A multi-center, doubleblind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Adv Ther. 2020;37(10):4249-4265.
- Data on file. Raleigh, NC: Merz Pharmaceuticals, LLC; 2021.
In patients previously treated with Botox®
XEOMIN Significantly Reduced Mean Symptom Severity
as Measured by JRS Severity Subscore3
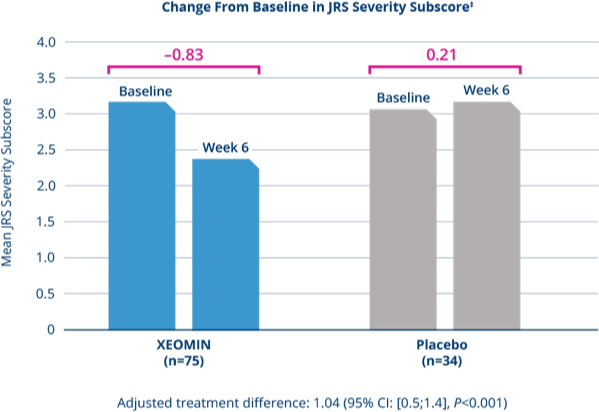

‡Missing values replaced with last observation carried forward.
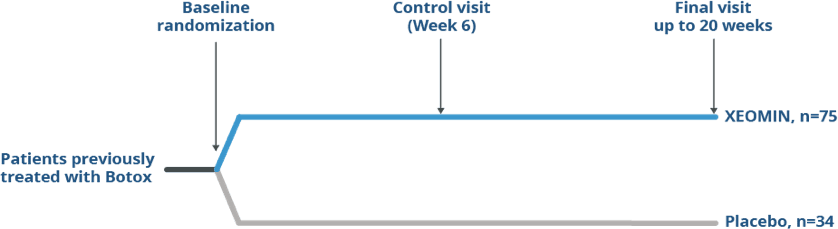
Pivotal Study Design in Patients
Previously Treated With Botox®
Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled
Trial of XEOMIN in Patients with Blepharospasm1



Reference
- Jankovic J, Comella C, Hanschmann A, Grafe S. Efficacy and safety of incobotulinumtoxinA (NT 201, Xeomin) in the treatment of blepharospasm⚊a randomized trial. Mov Disord. 2011;26(8):1521-1528.
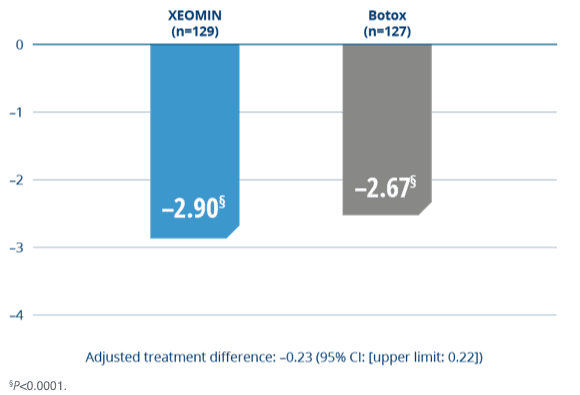
Noninferiority study: XEOMIN vs active comparator (Botox)
XEOMIN Was Proven Noninferior to Botox
- XEOMIN and Botox were similarly effective in treating blepharospasm as measured by the JRS sum score at Week 34
Change From Baseline in JRS Sum Score4

The potency Units of XEOMIN are specific to the preparation and assay method utilized. They are not interchangeable with the other preparations of botulinum toxin products and, therefore, Units of biological activity of XEOMIN cannot be compared to or converted into Units of any other botulinum toxin products assessed with any other specific assay method.
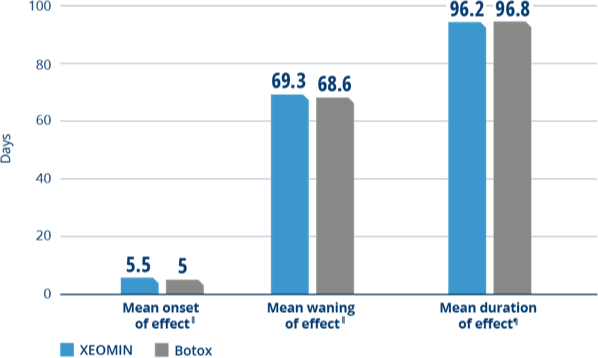
Noninferiority study: XEOMIN vs active comparator (Botox)
XEOMIN and Botox Had Similar
Onset, Waning, and Duration of Effect4

‖Patient-reported outcome: onset and waning of effect were subjectively estimated by the patient at control and end of study visits.
¶Duration of effect was calculated based on the time between the initial injection and the end of study visit (when the subject and the investigator agreed that a new injection was needed).
The duration of effect in patients with blepharospasm
was comparable between XEOMIN and Botox.4
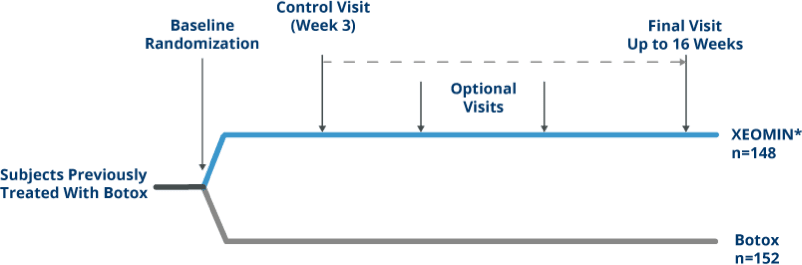
Noninferiority Study Design
Randomized, Double-blind, active-controlled
Noninferiority Trial of XEOMIN vs Botox in Patients with Blepharospasm4

*Intent-to-treat.


The potency Units of XEOMIN are specific to the preparation and assay method utilized. They are not interchangeable with the other preparations of botulinum toxin products and, therefore, Units of biological activity of XEOMIN cannot be compared to or converted into Units of any other botulinum toxin products assessed with any other specific assay method.
Reference
- Roggenkämper P, Jost WH, Bihari K, Comes G, Grafe S; for the NT 201 Blepharospasm Study Team. Efficacy and safety of a new botulinum toxin type A free of complexing proteins in the treatment of blepharospasm. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2006;113(3):303-312.
References
- Mitsikostas DD, Dekundy A, Sternberg K, Althaus M, Pagan F. IncobotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of blepharospasm in toxin-naïve subjects: a multi-center, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Adv Ther. 2020;37(10):4249-4265.
- XEOMIN® [Package insert]. Raleigh, NC: Merz Pharmaceuticals, LLC; 2021.
- Jankovic J, Comella C, Hanschmann A, Grafe S. Efficacy and safety of incobotulinumtoxinA (NT 201, Xeomin) in the treatment of blepharospasm-a randomized trial. Mov Disord. 2011;26(8):1521-1528.
- Roggenkämper P, Jost WH, Bihari K, Comes G, Grafe S; for the NT 201 Blepharospasm Study Team. Efficacy and safety of a new botulinum toxin type A free of complexing proteins in the treatment of blepharospasm. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2006;113(3):303-312.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION INCLUDING BOXED WARNING
WARNING: DISTANT SPREAD OF TOXIN EFFECT
See full prescribing information for complete BOXED WARNING.
The effects of XEOMIN and all botulinum toxin products may spread from the area of injection to produce symptoms consistent with botulinum toxin effects. These symptoms have been reported hours to weeks after injection. Swallowing and breathing difficulties can be life threatening and there have been reports of death. The risk of symptoms is probably greatest in children treated for spasticity but symptoms can also occur in adults, particularly in those patients who have underlying conditions that would predispose them to these symptoms.
Indications
XEOMIN® (incobotulinumtoxinA) for injection is indicated for the treatment of:
- Chronic sialorrhea in patients 2 years of age and older
- Upper limb spasticity in adults
- Upper limb spasticity in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older, excluding spasticity caused by cerebral palsy
- Cervical dystonia in adults
- Blepharospasm in adults
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Known hypersensitivity to any botulinum toxin product or to any of the components in the formulation.
- Infection at the proposed injection site(s) because it could lead to severe local or disseminated infection.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- The potency units of XEOMIN are specific to the preparation and assay method used and are not interchangeable with other preparations of botulinum toxin products. Therefore, Units of biological activity of XEOMIN cannot be compared to or converted into Units of any other botulinum toxin products.
- Serious hypersensitivity reactions have been reported with botulinum toxin products (anaphylaxis, serum sickness, urticaria, soft tissue edema, and dyspnea). If serious and/or immediate hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue further injection of XEOMIN and institute appropriate medical therapy immediately. The use of XEOMIN in patients with a known hypersensitivity to any botulinum neurotoxin or to any of the excipients (human albumin, sucrose), could lead to a life-threatening allergic reaction.
- Treatment with XEOMIN and other botulinum toxin products can result in swallowing or breathing difficulties. Patients with pre-existing swallowing or breathing difficulties may be more susceptible to these complications. When distant effects occur, additional respiratory muscles may be involved. Patients may require immediate medical attention should they develop problems with swallowing, speech, or respiratory disorders. Dysphagia may persist for several months, which may require use of a feeding tube. Aspiration may result from severe dysphagia [See BOXED WARNING].
- Individuals with peripheral motor neuropathic diseases, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or neuromuscular junctional disorders (e.g., myasthenia gravis or Lambert-Eaton syndrome) may be at increased risk for severe dysphagia and respiratory compromise from typical doses of XEOMIN.
- Cervical Dystonia: Treatment with botulinum toxins may weaken neck muscles that serve as accessory muscles of ventilation. This may result in critical loss of breathing capacity in patients with respiratory disorders who may have become dependent upon these accessory muscles. There have been post-marketing reports of serious breathing difficulties, including respiratory failure, in patients with cervical dystonia treated with botulinum toxin products. Patients with smaller neck muscle mass and patients who require bilateral injections into the sternocleidomastoid muscles are at greater risk of dysphagia. Limiting the dose injected into the sternocleidomastoid muscle may decrease the occurrence of dysphagia.
- Blepharospasm: Injection of XEOMIN into the orbicularis oculi muscle may lead to reduced blinking and corneal exposure with possible ulceration or perforation. To decrease the risk for ectropion, XEOMIN should not be injected into the medial lower eyelid area.
- XEOMIN contains human serum albumin. Based on effective donor screening and product manufacturing processes, it carries an extremely remote risk for transmission of viral diseases and variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD). There is a theoretical risk for transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD), but if that risk actually exists, the risk of transmission would also be considered extremely remote. No cases of transmission of viral diseases, CJD, or vCJD have ever been reported for albumin.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most commonly observed adverse reactions at rates specified below and greater than placebo are:
-
Chronic Sialorrhea:
- in adults (≥4% of patients): tooth extraction, dry mouth, diarrhea, and hypertension.
- in pediatric patients (≥1% of patients): bronchitis, headache, and nausea/vomiting.
-
Upper Limb Spasticity
- in adults (≥2% of patients): seizure, nasopharyngitis, dry mouth, and upper respiratory tract infection.
- in pediatric patients (≥3% of patients): nasopharyngitis and bronchitis.
- Cervical Dystonia in adults (≥5% of patients): dysphagia, neck pain, muscle weakness, injection site pain, and musculoskeletal pain.
- Blepharospasm in adults (≥10% of patients): eyelid ptosis, dry eye, visual impairment, and dry mouth.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Co-administration of XEOMIN and aminoglycoside or other agents interfering with neuromuscular transmission, (e.g., muscle relaxants), should only be performed with caution as these agents may potentiate the effect of the toxin.
Use of anticholinergic drugs after administration of XEOMIN may potentiate systemic anticholinergic effects.
The effect of administering different botulinum toxin products at the same time or within several months of each other is unknown. Excessive neuromuscular weakness may be exacerbated by administration of another botulinum toxin prior to the resolution of the effects of a previously administered botulinum toxin.
USE IN PREGNANCY
There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with the use of XEOMIN in pregnant women. XEOMIN should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
PEDIATRIC USE
Safety and effectiveness of XEOMIN in patients less than 18 years of age have not been established for lower limb spasticity, cervical dystonia, or blepharospasm.
Safety and effectiveness have been established in pediatric patients 2 to 17 years of age in patients with chronic sialorrhea and upper limb spasticity. A pediatric assessment for XEOMIN in upper limb spasticity demonstrates that XEOMIN is safe and effective in another pediatric population. However, XEOMIN is not approved for such patient population due to marketing exclusivity for another botulinum toxin.
