

Cervical Dystonia in Adults
Pivotal trial: XEOMIN vs placebo
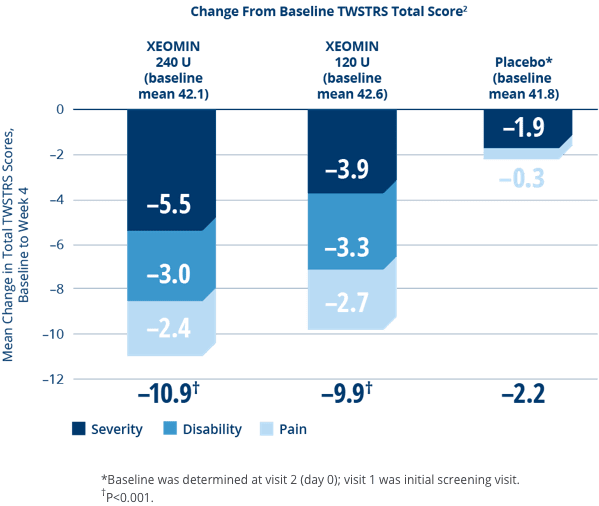
XEOMIN Significantly Improved Cervical Dystonia Symptoms vs Placebo1,2
- XEOMIN demonstrated improvements in cervical dystonia as measured by the primary endpoint, the Toronto Western Spasmodic Torticollis Rating Scale (TWSTRS)1,2
- No significant difference in effectiveness between doses2
- Similar efficacy in XEOMIN patients who were botulinum toxin-naÏve and those who had received botulinum toxin prior to this study2
- No gender- or age-related differences observed in response to XEOMIN. There were too few non-white patients to adequately assess efficacy in that population2
Pivotal Trial Design
Randomized, Placebo-controlled Trial of
XEOMIN in Patients with Cervical Dystonia1,2
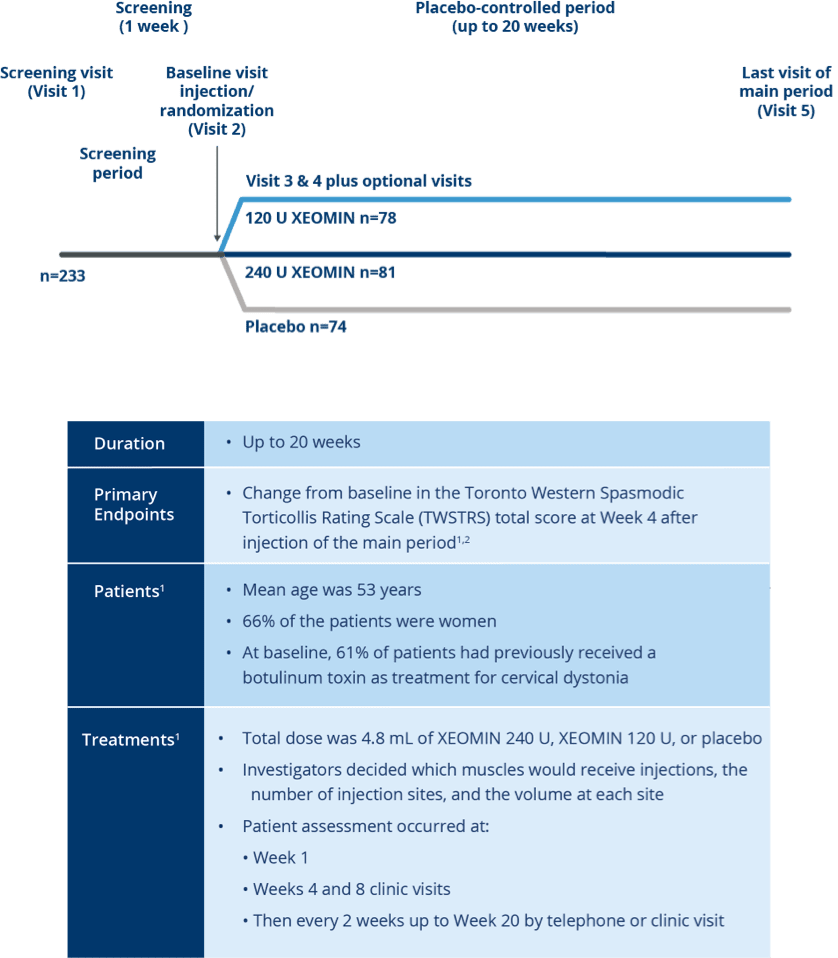

Studied in nearly 600 patients with
cervical dystonia worldwide3
References
- XEOMIN® [Package insert]. Raleigh, NC: Merz Pharmaceuticals, LLC; 2021.
- Comella CL, Jankovic J, Truong DD, Hanschmann A, Grafe S; US XEOMIN Cervical Dystonia Study Group. Efficacy and safety of incobotulinumtoxinA (NT 201, XEOMIN®, botulinum neurotoxin type A, without accessory proteins) in patients with cervical dystonia.
J Neurol Sci. 2011;308(1-2):103-109. - Data on file. Raleigh, NC: Merz Pharmaceuticals, LLC; 2021.
Noninferiority study: XEOMIN vs active comparator (Botox®)
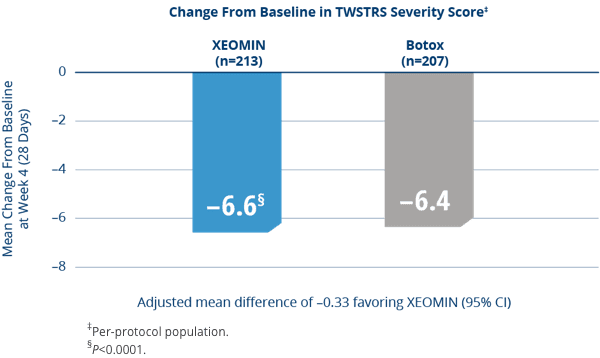
XEOMIN Was Proven Noninferior to the
Active Comparator (Botox) in Adults with Cervical Dystonia3
- XEOMIN and Botox were similarly effective in treating the symptoms of cervical dystonia as measured by TWSTRS severity score at Week 43
- The potency Units of XEOMIN are specific to the preparation and assay method utilized. They are not interchangeable with the other preparations of botulinum toxin products and, therefore, Units of biological activity of XEOMIN cannot be compared to or converted into Units of any other botulinum toxin products assessed with any other specific assay method
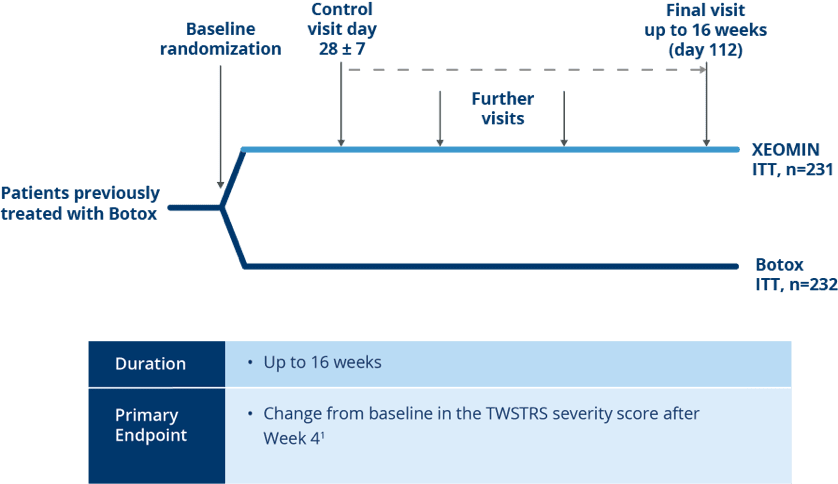
Noninferiority Trial Design
Randomized, Active-controlled Noninferiority Trial of XEOMIN vs Botox®
in Patients with Cervical Dystonia1
Reference
- Benecke R, Jost WH, Kaňovský P, Ruzicka E, Comes G, Grafe S. A new botulinum toxin type A free of complexing proteins for treatment of cervical dystonia. Neurology. 2005;64(11):1949-1951.
ITT, intent–to–treat; TWSTRS, Toronto Western Spasmodic Torticollis Rating Scale. TWSTRS total score includes subscales of Severity, Disability, and Pain. The potency Units of XEOMIN are specific to the preparation and assay method utilized. They are not interchangeable with the other preparations of botulinum toxin products and, therefore, Units of biological activity of XEOMIN cannot be compared to or converted into Units of any other botulinum toxin products assessed with any other specific assay method.
Comparable Duration of Effect Between XEOMIN and Botox
in Patients with Cervical Dystonia3
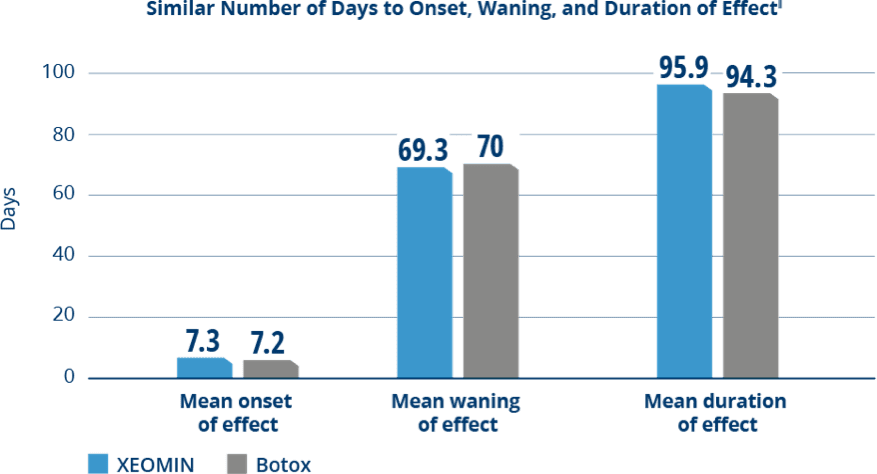
‖Time to onset of effect was the time from injection until start of treatment effect; the time to waning of effect was the time from injection until decline of effect; and the duration of effect was the interval between injection and the first visit at which the TWSTRS severity score had reached at least 80% of the baseline value.
References
- XEOMIN® [Package insert]. Raleigh, NC: Merz Pharmaceuticals, LLC; 2021.
- Comella CL, Jankovic J, Truong DD, Hanschmann A, Grafe S; US XEOMIN Cervical Dystonia Study Group. Efficacy and safety of incobotulinumtoxinA (NT 201, XEOMIN®, botulinum neurotoxin type A, without accessory proteins) in patients with cervical dystonia. J Neurol Sci. 2011;308(1-2):103-109.
- Benecke R, Jost WH, Kañovský P, Ruzicka E, Comes G, Grafe S. A new botulinum toxin type A free of complexing proteins for treatment of cervical dystonia. Neurology. 2005;64(11):1949–1951.
