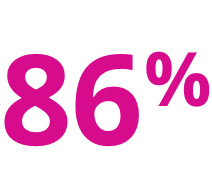
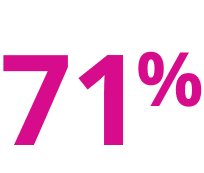
XEOMIN® (incobotulinumtoxinA) IMPORTANT CONSUMER SAFETY INFORMATION
Warnings
XEOMIN may cause serious side effects that can be life threatening. Get medical help right away if you have any of these problems any time (hours to weeks) after injection of XEOMIN:
-
Problems swallowing, speaking, or breathing can happen if the muscles that you use to breathe and swallow become weak. Death can happen as a complication if you have severe problems with swallowing or breathing after treatment with XEOMIN.
- People with certain breathing problems may need to use muscles in their neck to help them breathe and may be at greater risk for serious breathing problems with XEOMIN.
- Swallowing problems may last for several months, and during that time you may need a feeding tube to receive food and water. If swallowing problems are severe, food or liquids may go into your lungs. People who already have swallowing or breathing problems before receiving XEOMIN have the highest risk of getting these problems.
- Spread of toxin effects. In some cases, the effect of botulinum toxin may affect areas of the body away from the injection site and cause symptoms of a serious condition called botulism. The symptoms of botulism include: loss of strength and muscle weakness all over the body, double vision, blurred vision and drooping eyelids, hoarseness or change or loss of voice, trouble saying words clearly, loss of bladder control, trouble breathing, trouble swallowing.
These symptoms can happen hours to weeks after you receive an injection of XEOMIN. These problems could make it unsafe for you to drive a car or do other dangerous activities.
Read the Medication Guide before you start receiving XEOMIN® (Zeo-min) and each time XEOMIN is given to you as there may be new information. The risk information provided here is not comprehensive. To learn more:
- Talk to your health care provider or pharmacist
- Visit www.xeomin.com to obtain the FDA-approved product labeling
- Call 1-855-4MERZTX (1-855-463-7989)
Uses
XEOMIN is a prescription medicine:
- that is injected into glands that make saliva and is used to treat long-lasting (chronic) drooling (sialorrhea) in adults and in children 2 to 17 years of age.
-
that is injected into muscles and used to:
- treat increased muscle stiffness in the arm because of upper limb spasticity in adults.
- treat increased muscle stiffness in the arm in children 2 to 17 years of age with upper limb spasticity, excluding spasticity caused by cerebral palsy.
- treat the abnormal head position and neck pain with cervical dystonia (CD) in adults.
- treat abnormal spasm of the eyelids (blepharospasm) in adults.
It is not known if XEOMIN is safe and effective in children younger than:
- 2 years of age for the treatment of chronic sialorrhea
- 2 years of age for the treatment of upper limb spasticity
- 18 years of age for the treatment of cervical dystonia or blepharospasm
Do not take XEOMIN if you: are allergic to XEOMIN or any of the ingredients in XEOMIN (see below for a list of ingredients in XEOMIN), had an allergic reaction to any other botulinum toxin product such as rimabotulinumtoxinB (Myobloc®), onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox®, Botox® Cosmetic), or abobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport®) or have a skin infection at the planned injection site.
Before receiving XEOMIN, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have a disease that affects your muscles and nerves (such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [ALS or Lou Gehrig's disease], myasthenia gravis or Lambert-Eaton syndrome)
- have had any side effect from any other botulinum toxin in the past
- have a breathing problem, such as asthma or emphysema
- have a history of swallowing problems or inhaling food or fluid into your lungs (aspiration)
- have drooping eyelids
- have had eye surgery
- have had surgery on your face
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if XEOMIN can harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if XEOMIN passes into breast milk.
Tell your doctor about all of the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Talk to your doctor before you take any new medicines after you receive XEOMIN.
Using XEOMIN with certain other medicines may cause serious side effects. Do not start any new medicines until you have told your doctor that you have received XEOMIN in the past.
Especially tell your doctor if you:
- have received any other botulinum toxin product in the last four months
- have received injections of botulinum toxin such as rimabotulinumtoxinB (MYOBLOC®), onabotulinumtoxinA (BOTOX®, BOTOX® COSMETIC) and abobotulinumtoxinA (DYSPORT®) in the past. Be sure your doctor knows exactly which product you received. The dose of XEOMIN may be different from other botulinum toxin products that you have received.
- have recently received an antibiotic by injection or inhalation
- take muscle relaxants
- take an allergy or cold medicine
- take a sleep medicine
Ask your doctor if you are not sure if your medicine is one that is listed above.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines with you to show your doctor and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine.
Possible Side Effects
XEOMIN can cause serious side effects including:
- Injury to the cornea (the clear front surface of the eye) in people treated for blepharospasm. People who receive XEOMIN to treat spasm of the eyelid may have reduced blinking that can cause a sore on their cornea or other problems of the cornea. Call your healthcare provider or get medical care right away if you have eye pain or irritation after treatment with XEOMIN.
- XEOMIN may cause other serious side effects including allergic reactions. Symptoms of an allergic reaction to XEOMIN may include: itching, rash, redness, swelling, wheezing, trouble breathing, or dizziness or feeling faint. Tell your doctor or get medical help right away if you get wheezing or trouble breathing, or if you get dizzy or faint.
The most common side effects of XEOMIN in adults with chronic sialorrhea include:
- needing to have a tooth pulled (extracted)
- dry mouth
- diarrhea
- high blood pressure
The most common side effects of XEOMIN in children 2 to 17 years of age with chronic sialorrhea include:
- bronchitis
- nausea
- headache
- vomiting
The most common side effects of XEOMIN in adults with upper limb spasticity include:
- seizure
- nasal congestion, sore throat and runny nose
- dry mouth
- upper respiratory infection
The most common side effects of XEOMIN in children 2 to 17 years of age with upper limb spasticity include:
- nasal congestion, sore throat and runny nose
- bronchitis
The most common side effects of XEOMIN in adults with cervical dystonia include:
- difficulty swallowing
- neck pain
- muscle weakness
- pain at the injection site
- muscle and bone pain
The most common side effects of XEOMIN in adults with blepharospasm include:
- drooping of the eyelid
- dry eye
- vision problems
- dry mouth
These are not all the possible side effects of XEOMIN.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1–800–FDA–1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of XEOMIN
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about XEOMIN that is written for health professionals.
Active Ingredient: botulinum toxin type A
Inactive Ingredients: human albumin and sucrose
Please see Full Prescribing Information and Medication Guide.